


|
|
|
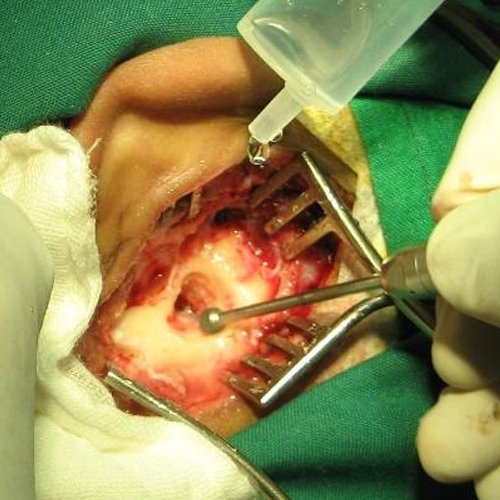 A mastoidectomy is a procedure performed to remove the mastoid air cells, air bubbles in the skull, near the inner ears. This can be done as part of treatment for mastoiditis, chronic suppurative otitis media or cholesteatoma.
A mastoidectomy is a procedure performed to remove the mastoid air cells, air bubbles in the skull, near the inner ears. This can be done as part of treatment for mastoiditis, chronic suppurative otitis media or cholesteatoma.
In addition, it is sometimes performed as part of other procedures (cochlear implant) or for access to the middle ear. There are classically 5 different types of mastoidectomy:
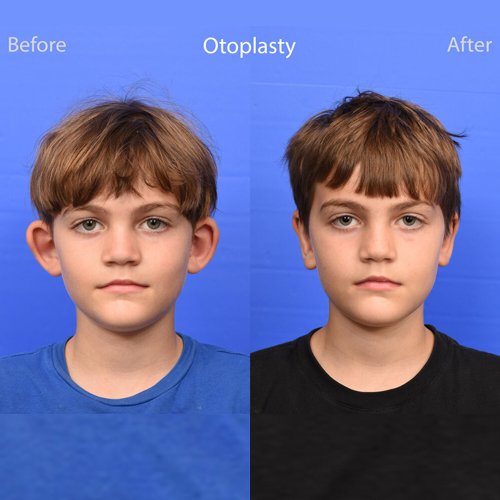 Ear surgery, also known as otoplasty, can improve the shape, position or proportion of the ear. A defect in the ear structure that is present at birth or that becomes apparent with development can be corrected by otoplasty. This procedure can also treat misshapen ears caused by injury.
Ear surgery, also known as otoplasty, can improve the shape, position or proportion of the ear. A defect in the ear structure that is present at birth or that becomes apparent with development can be corrected by otoplasty. This procedure can also treat misshapen ears caused by injury.
Otoplasty creates a more natural shape while bringing balance and proportion to the ears and face. Correction of even minor deformities can have profound benefits to appearance and self-esteem. If protruding or disfigured ears bother you or your child, you may consider plastic surgery.
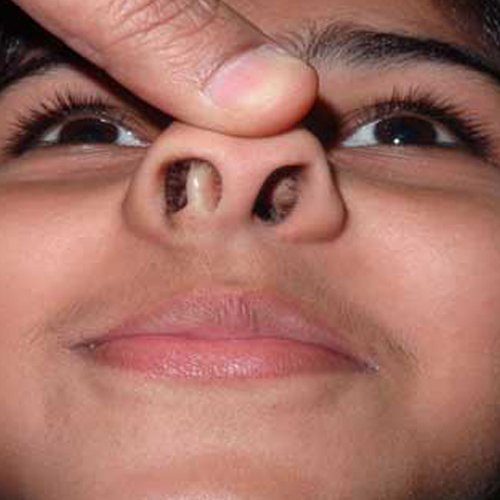 Deviated nasal septum is a very common problem. If the patient is having mild symptoms which is not very troubling, we would advise simple medications like nasal sprays, nasal washes, and antihistamines. But if the patient is having very troubling symptoms, like difficulty in sleeping, or if patient having difficulty in performing regular activities normally, then we would advise a surgery called septoplasty.
Deviated nasal septum is a very common problem. If the patient is having mild symptoms which is not very troubling, we would advise simple medications like nasal sprays, nasal washes, and antihistamines. But if the patient is having very troubling symptoms, like difficulty in sleeping, or if patient having difficulty in performing regular activities normally, then we would advise a surgery called septoplasty.
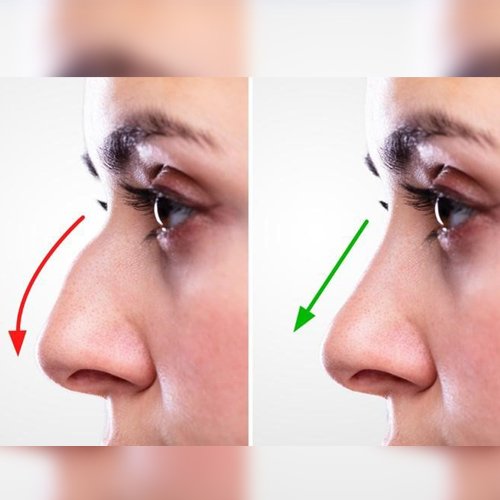 Rhinoplasty (RIE-no-plas-tee) is surgery that changes the shape of the nose. The motivation for rhinoplasty may be to change the appearance of the nose, improve breathing or both.
The upper portion of the structure of the nose is bone, and the lower portion is cartilage. Rhinoplasty can change bone, cartilage, skin or all three. Talk with your surgeon about whether rhinoplasty is appropriate for you and what it can achieve.
Rhinoplasty (RIE-no-plas-tee) is surgery that changes the shape of the nose. The motivation for rhinoplasty may be to change the appearance of the nose, improve breathing or both.
The upper portion of the structure of the nose is bone, and the lower portion is cartilage. Rhinoplasty can change bone, cartilage, skin or all three. Talk with your surgeon about whether rhinoplasty is appropriate for you and what it can achieve.
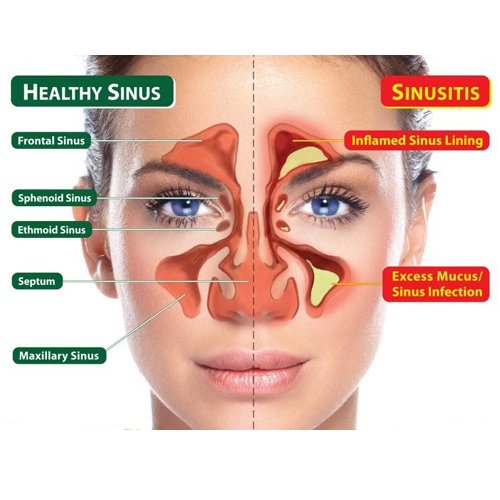 Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS) is a minimally invasive surgery used to treat recurrent or persistent sinus infections, abnormal growth of tissues in the nose (nasal polyps) and to remove tumours. In this procedure, an endoscope is used to operate on the sinuses through the nostrils. There are no external scars.
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS) is a minimally invasive surgery used to treat recurrent or persistent sinus infections, abnormal growth of tissues in the nose (nasal polyps) and to remove tumours. In this procedure, an endoscope is used to operate on the sinuses through the nostrils. There are no external scars.
 Throat surgery treats a wide variety of conditions, from life-threatening cancers to chronic sore throats and breathing difficulties.
Throat surgery treats a wide variety of conditions, from life-threatening cancers to chronic sore throats and breathing difficulties.
Because throat surgery may be an option for many types of diseases, we've compiled some of the most common reasons throat surgery may be needed.
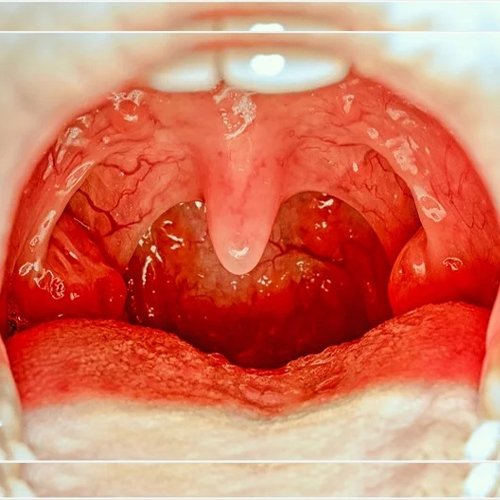 Tonsillectomy (ton-sih-LEK-tuh-me) is the surgical removal of the tonsils, two oval-shaped pads of tissue at the back of the throat — one tonsil on each side.
Tonsillectomy (ton-sih-LEK-tuh-me) is the surgical removal of the tonsils, two oval-shaped pads of tissue at the back of the throat — one tonsil on each side.
A tonsillectomy was once a common procedure to treat infection and inflammation of the tonsils (tonsillitis). Today, a tonsillectomy is usually performed for sleep-disordered breathing but may still be a treatment when tonsillitis occurs frequently or doesn't respond to other treatments.
A tonsillectomy may also be necessary to treat breathing and other problems related to enlarged tonsils and to treat rare diseases of the tonsils.
Recovery time for a tonsillectomy is usually at least 10 days to two weeks.
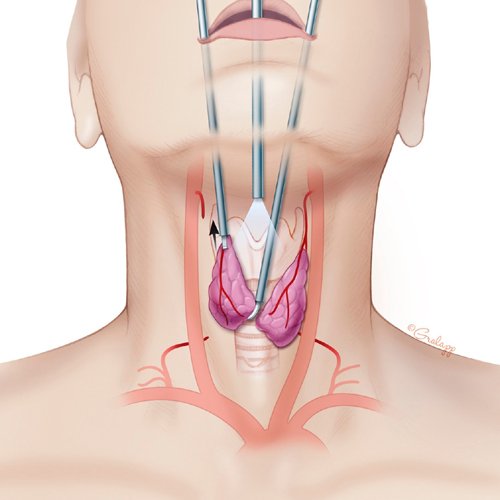
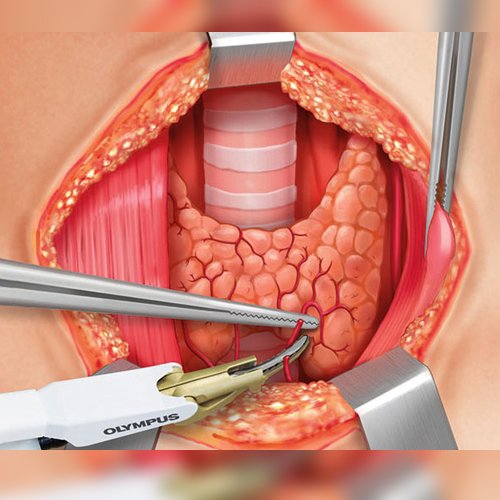 Thyroidectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of your thyroid gland. Your thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of your neck. It makes hormones that control every part of your metabolism, from your heart rate to how quickly you burn calories.
Thyroidectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of your thyroid gland. Your thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of your neck. It makes hormones that control every part of your metabolism, from your heart rate to how quickly you burn calories.
Health care providers perform thyroidectomy to treat thyroid disorders. These include cancer, noncancerous enlargement of the thyroid (goiter) and overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism).
How much of your thyroid gland is removed during thyroidectomy depends on the reason for the surgery. If you need only part of your thyroid removed (partial thyroidectomy), your thyroid may work normally after surgery.
If you need your entire thyroid removed (total thyroidectomy), you need daily treatment with thyroid hormone to replace your thyroid's natural function.
 Rameshwaram Super Speciality Hospital is nationally recognized for expertise in a full range of medical and surgical services for people with problems of the ear, nose, sinus, head and neck.
Rameshwaram Super Speciality Hospital is nationally recognized for expertise in a full range of medical and surgical services for people with problems of the ear, nose, sinus, head and neck.
Our otolaryngology (ENT)/head and neck surgeons perform hundreds of more common procedures, such as removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy), repair of eardrum (tympanic membrane) perforations and sinus surgery.
And they do highly complex surgeries, such as endoscopy for pituitary tumours, robotic surgery for throat cancer and microsurgery for acoustic neuroma tumours.
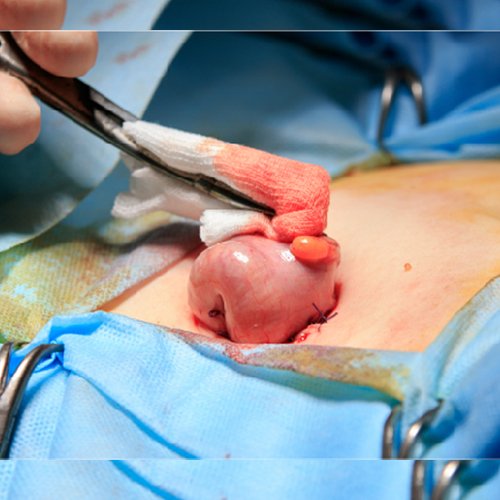 Cancer surgery is an operation or procedure to take out a tumor and possibly some nearby tissue. It is the oldest kind of cancer treatment, and it still works well to treat many types of cancer today. A doctor who specializes in cancer surgery is called a "surgical oncologist."
Cancer surgery is an operation or procedure to take out a tumor and possibly some nearby tissue. It is the oldest kind of cancer treatment, and it still works well to treat many types of cancer today. A doctor who specializes in cancer surgery is called a "surgical oncologist."
You might have surgery to remove a tumor, help your body work the way it used to, or relieve side effects. Surgery can be performed in a doctor's office, clinic, surgery center, or hospital. Where you go depends on the type of surgery and how much time you need to heal. Your surgery may require medication to block the awareness of pain, called anesthesia. There are different types of anesthesia depending on the type and extent of the surgery.
If you need to stay in the hospital overnight or for several days after surgery, it is called inpatient surgery. Or you might not need to stay in the hospital at all. If you can go home the same day, it is called outpatient surgery or ambulatory surgery.
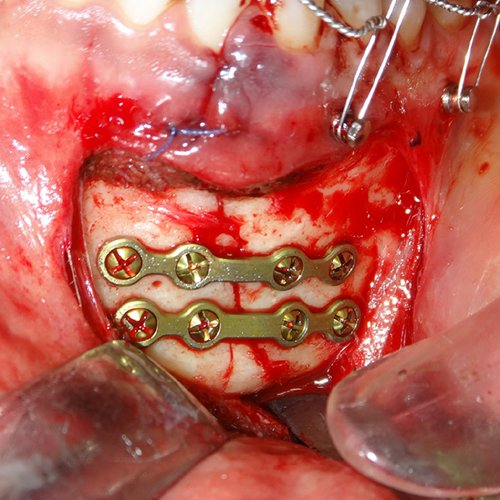 A broken jaw is a break (fracture) in the jaw bone. A dislocated jaw means the lower part of the jaw has moved out of its normal position at one or both joints where the jaw bone connects to the skull (temporomandibular joints). Surgery is often needed for moderate to severe fractures.
A broken jaw is a break (fracture) in the jaw bone. A dislocated jaw means the lower part of the jaw has moved out of its normal position at one or both joints where the jaw bone connects to the skull (temporomandibular joints). Surgery is often needed for moderate to severe fractures.
The jaw may be wired to the teeth of the opposite jaw to keep the jaw stable while it heals.
Jaw wires are usually left in place for 6 to 8 weeks. Small rubber bands (elastics) are used to hold the teeth together.
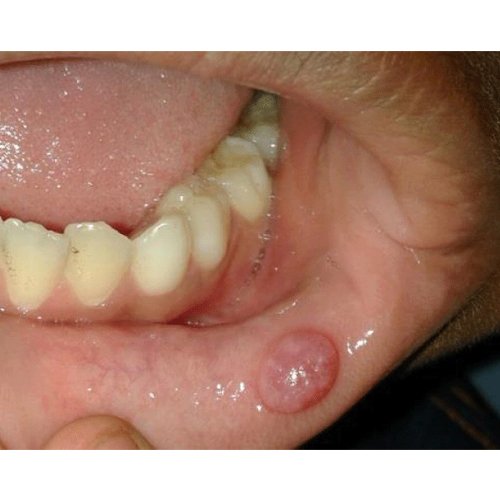 A mucocele is a mucus cyst produced by extravasation of salivary secretion due to the rupture of a salivary gland duct, or salivary retention within an accessory salivary gland, due to duct stricture or sialoliths. The mucocele appearance is highly characteristic in most cases, and diagnosis is made on clinical grounds.
A mucocele is a mucus cyst produced by extravasation of salivary secretion due to the rupture of a salivary gland duct, or salivary retention within an accessory salivary gland, due to duct stricture or sialoliths. The mucocele appearance is highly characteristic in most cases, and diagnosis is made on clinical grounds.
The most common mode of removal is surgical mucocele excision.
This involves the removal of the cyst, the mucosa around it, and the glandular tissue until the muscular layer is reached.
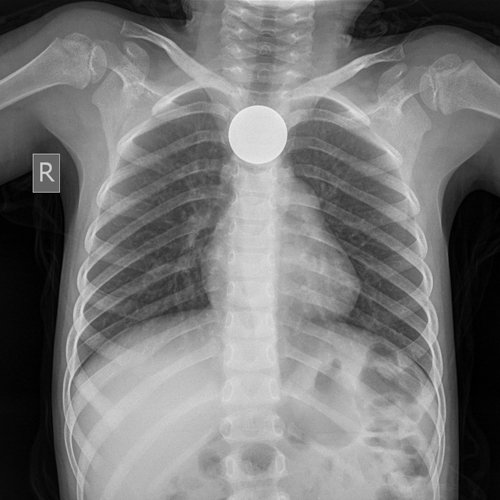 Most patients who present for evaluation of a foreign body in the esophagus do so after accidental ingestion of a known object, and the patient has mild symptoms and is in stable condition.
Most patients who present for evaluation of a foreign body in the esophagus do so after accidental ingestion of a known object, and the patient has mild symptoms and is in stable condition.
The challenges come from patients who are unable or unwilling to provide a history of the object ingested or when it occurred.
Examples are infants, children, mentally impaired, psychiatric, and prisoners. Also, the wide range of possible symptoms and clinical presentations, plus the wide range of potential complications, can make this a difficult condition to evaluate and manage.
This activity reviews the etiology, presentation, evaluation, and management of esophageal foreign body ingestion and reviews the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating, diagnosing, and managing the condition.
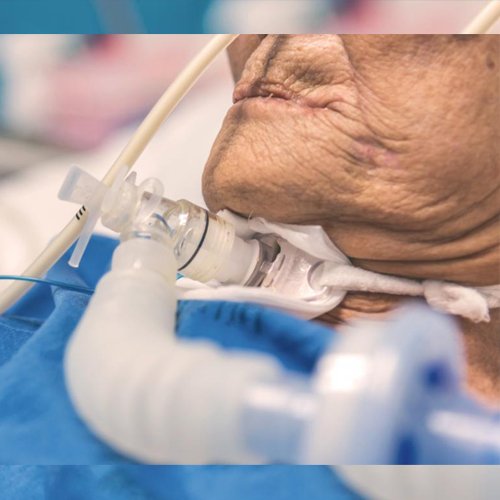 A tracheostomy is an opening created at the front of the neck so a tube can be inserted into the windpipe (trachea) to help you breathe.
A tracheostomy is an opening created at the front of the neck so a tube can be inserted into the windpipe (trachea) to help you breathe.
If necessary, the tube can be connected to an oxygen supply and a breathing machine called a ventilator.
The tube can also be used to remove any fluid that's built up in the throat and windpipe. Tracheotomy is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision on the anterior aspect of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea.
Why a tracheostomy is used ?
A tracheostomy will usually be planned in advance and carried out in hospital. But sometimes it may need to be done in an emergency outside of hospital, such as at the scene of an accident.
Designed by Seacom Digital